

| English version |
Kapazität C, Frequenz f und kapazitiver Blindwiderstand XC
Gib die Werte für Widerstand und Kondensator ein, dann drücke "Berechnen".
Bei Dezimal-Eingabe ist stets der Punkt zu verwenden.
| Der Blindwiderstand (auch Reaktanz) XC ist eine Größe der Elektrotechnik, die einen Wechselstrom durch Aufbau einer Wechselspannung begrenzt und eine zeitliche Verschiebung zwischen Spannung und Strom verursacht. Der Wert des Blindwiderstandes ist frequenzabhängig. Kapazitive Reaktanz XC ist umgekehrt proportional zur Frequenz f (oder der Kreisfrequenz ω) und der Kapazität C. |
Kapazitiver Blindwiderstand (Reaktanz) 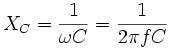
Scheinwiderstand (Impedanz) ![]()
Scheinwiderstand Z - Berechnung für C und L
Frequenzgang und Entzerrung EQ - Präemphase (Preemphasis) und Deemphase (Deemphasis)
| 1 000 000 pF = 1 000 nF = 1 µF = 1·10−6 F 100 000 pF = 100 nF = 0,1 µF = 1·10−7 F 10 000 pF = 10 nF = 0,01 µF = 1·10−8 F 1 000 pF = 1 nF = 0,001 µF = 1·10−9 F 100 pF = 0,1 nF = 0,000 1 µF = 1·10−10 F 10 pF = 0,01 nF = 0,000 01 µF = 10·10−11 F 1 pF = 0,001 nF = 0,000 001 µF = 1·10−12 F |
| SI-Präfixe für Hertz (Hz) | ||
| Wert | Symbol | Name |
| 103 Hz | kHz | Kilohertz |
| 106 Hz | MHz | Megahertz |
| 109 Hz | GHz | Gigahertz |
| 1012 Hz | THz | Terahertz |
| Die üblichen Einheiten | ||
Kapazität eines Kondensators C = Q / U
Kapazität C, Elektrische Ladung Q, und Spannung U.
Bitte zwei Werte eingeben, der dritte Wert wird berechnet.
| Eine typische Frage: "Wie messe ich einen Kondensator?" http://lmgtfy.com/?q=Kapazit%C3%A4t+messen&filter=0 |
| zurück |
Suchmaschine |
Startseite |