

| Deutsche Version |
|
|
| With "dB" and "ratio" near the input boxes, we decide what is calculated and which box is the input. With size of a "field" and size of "energy" we decide if it is 20 times (field quantity, e.g. volts) or 10 times (energy quantity, or power quantity, e.g. watts) in the formula. |
The formulas for voltage and power
and the level calculation
| To use the calculator, simply enter a value. The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign. |
dBm indicates that the reference power is P0 = 1 milliwatt = 0.001 watt ≡ 0 dBm.
 |
 |
|
| Level of field quantity |
Level of energy quantity |
Sound pressure, sound intensity, and their levels:
Conversions and calculations of sound quantities and their levels
| Sound field quantities
Sound pressure, sound or particle velocity, particle displacement or displacement amplitude, (voltage, current, electric resistance). Inverse Distance Law 1/r |
Sound energy quantities Sound intensity, sound energy density, sound energy, acoustic power. (electrical power). Inverse Square Law 1/r² |
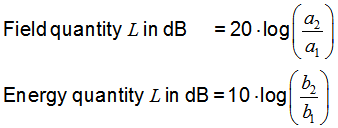
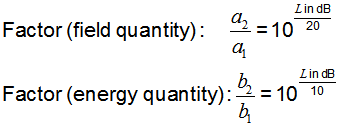
a1 and b1 is the reference
'a' could be a voltage V and 'b' could be a power P. P ~ V2
| Sound pressure Sound field size |
Sound pressure level | 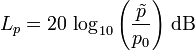 |
| Reference sound pressure p0 = 20 μPa = 2 × 10-5 Pa ≡ 0 dB Field sizes as the sound pressure, will always be shown as RMS value. The sound pressure p is the sound pressure that is specified as an rms value and of the static pressure pSt (air pressure) of the surrounding air is superimposed. ptotal = pSt + p |
| Sound intensity Sound energy size |
Sound intensity level |
| Sound field sizes: sound pressure, particle velocity, particle amplitude. Field sizes, such as the sound pressure are always expressed in RMS. This is mainly proportional to the electric voltage V. Sound energy sizes: sound intensity, sound energy, sound energy density, acoustic power. This is mainly proportional to the electric power P. |
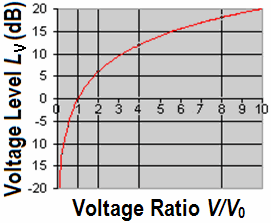
| Decibel scale for linear field sizes, like volts and sound pressures |
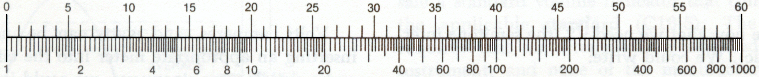 |
| The logarithmic scale (ratio) |
| Note - Comparing dB and dBA: There is no conversion formula for measured dBA values to sound pressure level dBSPL or vice versa. |
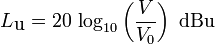
|
| Sound pressure and sound pressure level 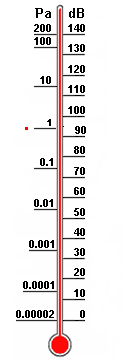 |
|
| Acousticians and sound protectors ("noise fighters") need the sound intensity (acoustic intensity) – but as a sound engineer and sound designer ("ear people") you don't need that sound energy quantity. Who is involved in audio engineering, should rather take care of the sound field quantity, that is the sound pressure or the sound pressure level (SPL) as an effect at the eardrums of our hearing and on the diaphragms of the microphones and the corresponding audio voltage and its voltage level. |
| Power is like all energy sizes primarily a calculated value. |
| In sound engineering there is no Power matching or Impedance matching. In audio we use only Voltage bridging or high Impedance bridging. |
|
Charts: Conversion of voltage or power ratios to decibels dB Decibel (dB) level conversion to volt Conversion: Voltage V to Level dB, dBu, dBV, and dBm |
| The defining equation for the level in decibels for field sizes (here voltage) is: LV = 20 × log10(V/V0) (dB) (Z1 = Z2) where V is the voltage being measured, and V0 is the reference to which V is being compared. The equation for obtaining voltage ratio V/V0 from the level LV in dB is: V/V0 = 10(LV/20) The defining equation for the level in decibels for energy sizes (here power) is: LP = 10 × log10(P/P0) (dB) where P is the power being measured, and P0 is the reference to which P is being compared. The equation for obtaining power ratio P/P0 from the level LP in dB is: P/P0 = 10(LP/10) |
| We do audio, not RF. We usually want to know VOLTAGE ratio, not POWER ratio. It turns out that if we have the same impedance level for one voltage and another, the ratio of the voltages can be accurately expressed as twenty times the log to base ten of the voltage ratios.So if we have an input voltage of 0.1 V from a 600 ohm source, and we get an output power of 32 V into a 600 ohms load, the voltage ratio is 20 × log 10 (32/0.1) = 20 × log (320) = 20 × 2.505 = 50 dB. Although it is only correct to speak of decibels in instances where the input and output impedances are the same, the audio world has ignored that (!), and we speak of voltage ratios without regard to the impedance. So a "power amplifier" which needs an input of 1.5 V from a 1000 ohms source to give an output of 30 V into 8 ohms is spoken of as having a gain of 20 × log (30/1.5) = 20 × log (20) = 20 × 1.3 = 26 dB. So "dB" is simply another way to write "ratio of". |
| Change in dB | Change in factor |
|---|---|
| 3 dB increase ≡ | Sound energy doubled: factor √2 |
| 3 dB decrease ≡ | Sound energy halved: factor √0.5 |
| 6 dB increase ≡ | Sound pressure doubled: factor 2 |
| 6 dB decrease ≡ | Sound energy halved: factor 0.5 |
| 10 dB increase ≡ | Loudness perception doubled: factor of 10 |
| 10 dB decrease ≡ | Loudness perception halved: factor of 0.1 |
|
| From: http://www.bv-elbtal.de/html/was_ist_larm_.html |
| back |
Search Engine |
home |